Demerits of Continuous Miner N in Indian Coal Mines

The coal mining sector accounts for more than 55% of India's energy needs even today. Read here to know about the new reforms in the sector.
In news:
High global prices may lead to domestic crunch: A sharp uptick in international and domestic coal prices due to the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict is set to impact import-dependent power producers as well as steel, cement, and aluminum producers.
What is Coal?
Coal is one of the most important primary fossil fuels, a solid carbon-rich material that is usually brown or black and most often occurs in stratified sedimentary deposits.
Coal is a natural resource that can be used as a source of energy, and in the production of coke for metallurgical processes. Coal is a major source of energy in the production of electrical power using steam generation.
In addition, gasification and liquefaction of coal produce gaseous and liquid fuels that can be transported by pipeline and stored in tanks.
Coal mining in India
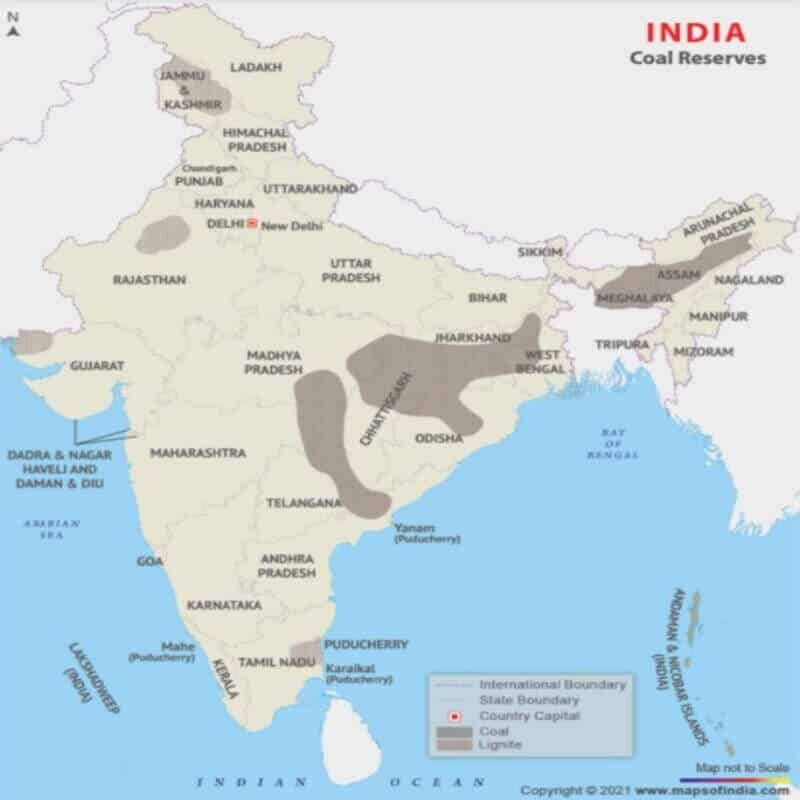
India is rich in ancient coal fields like Gondwana coalfields (250 million years old) and tertiary coalfields (15-60 million years old).
Coal mining was started during the rule of the East India Company in 1774 in the Raniganj coalfield along the western bank of the Damodar river.
To increase coal production, the focus of the Government is on accelerating domestic production of coal through the allocation of more coal blocks, pursuing with the State Government for assistance in land acquisition, and coordinated efforts with Railways for the movement of coal.
In addition, the following actions have been taken by Government to further enhance the production of coal in the country.
Commercial Auction of coal on revenue share mechanism:Since the launch of the auction of coal mines for commercial mining in June 2020, a total of 4 rounds of auctions have been conducted in which a total of 292 coal mines were offered.
Allowed sale of excess coal production: The Ministry of Coal has amended Mineral Concession Rules, 1960 to allow the sale of coal or lignite, on payment of an additional amount to the State Government.
- The Mines and Minerals (Development & Regulation) Act had been amended and is applicable for both the private and public sector captive mines.
- With this amendment, the Government has paved the way for releasing additional coal in the market by greater utilization of mining capacities of captive coal and lignite blocks, which were being only partly utilized owing to limited production of coal for meeting only their captive needs.
Rolling Auctions: To expedite the process for conducting auctions and to carry out more rounds of auctions in a year, a mechanism of rolling auctions of coal mines has been planned.
Single Window Clearance: The Union government has launched a Single Window Clearance portal for the coal sector to speed up the operationalization of coal mines. It is a unified platform that facilitates grants of clearances and approvals required for starting a coal mine in India.
Coal India Limited (CIL) has envisaged a coal production program of one Billion Tonne from CIL mines. CIL has taken the following steps to achieve the target of augmentation of coal production capacity.
- 15 Projects identified with a Capacity of about 160 MTPA (Million Tonnes per Annum) to be operated by Mine Developer cum Operator mode.
- Capacity addition through special dispensation in Environment Clearance under Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) 2006
- CIL has taken steps to upgrade the mechanized coal transportation and loading system under the 'First Mile Connectivity' projects.
Coal energy sector in India
In India, the energy transition away from coal is not happening in the foreseeable future. Although there will be a push for renewable/non-fossil-based energy, the share of coal in the energy basket is going to remain significant in the years ahead.
- Coal demand in the country is yet to peak as the Economic Survey 2021-22 projects coal demand in the range of 1.3-1.5 billion tonnes by 2030, an increase of 63 percent from the current demand.
Thus, as of now, there is no scenario of energy transition away from coal affecting any stakeholders involved in coal mining.
But India still imports a large amount of coal from outside and many companies have acquired coal mines overseas to ensure a continuous supply. This scenario exists due to the low productivity of coal and other factors like environmental issues affecting the mining activities.
Latest technologies to improve the quality of coal mining
Coal Companies are trying to adopt best mining practices and technology for coal mining and they have taken the following steps for improvement in the quality of coal mining –
- The technologies used in Opencast Coal Mining are modern and coal companies are keeping pace with technological advancement.
- Deployment of High capacity Heavy Earth Moving Machinery (HEMMs) like 42 cum Shovel with 240 T Rear Dumper.
- Surface Miners are being adopted in a big way to eliminate the need for hazardous blasting for coal extraction, customer satisfaction, and cater to environmental needs.
- First Mile Connectivity (FMC) projects – Coal transportation through in-pit crushing and conveying system/surface belt conveyor of all the future and existing mines.
- 3D terrestrial laser scanner for greater accuracy in Over Burden (OB) measurement.
- Introduction of drone/ Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for improved mine mapping and monitoring – land reclamation, fire mapping, mine closure monitoring.
- Several other technological interventions have also been made to increase work efficiency and mitigate the risk of accidents, e.g. Slope monitoring technologies, technology such as collision avoidance systems in dumpers, proximity warning systems, Operator independent Truck dispatch systems (OITDS), etc.
- An automated Mist-based Water sprinkling system for dust suppression is being deployed.
Coal Companies have been taking assistance from International Agencies/companies for guiding and monitoring the adoption of best mining practices and technology for coal mining.
Efforts to reduce pollution due to coal mining
Coal mining has impacts on the native environment, which are generally contained within the mining area itself.
The impact of mining activities involving drilling, blasting, loading, and transport of coal is the generation and dispersion of suspended particulate matter in the atmosphere for which various air pollution control measures have been prescribed.
- Generation and propagation of dust are controlled at the source by the installation of fixed sprinklers at CHPs, coal stockyards, weighbridges, and along transportation roads.
- Mobile water sprinklers are deployed along the haul roads and road transport road
- Long-throw fog canons have been deployed in mines and industrial establishments The mist-type water spraying system has been installed along with the conveyor belts / Bunkers in major coal handling plants. The sides of CHPs are covered by side cladding with GI Sheet to control pollution at the source.
- Control blasting techniques with proper delay detonators and explosives are used for the mitigation of dust generation and ground vibration during blasting operations.
- Coal companies are deploying modern equipment having environment-friendly features, like Surface Miner in coal that eliminates the drilling, blasting, and crushing operations in coal and hence, in turn, obviates pollution caused due to these operations.
- Use of drills fitted with wet drilling and dust extractors to control the generation of dust.
- To avoid spillage of Coal from trucks on road – all loaded coal transporting trucks are covered by tarpaulin and also overloading of trucks are prohibited
- Transport haul roads are kept well maintained and Concrete/blacktopped roads are being developed for better stability and durability;
- Mines have deployed mechanical sweepers and other methods for dry sweeping of roads.
- First Mile Connectivity (FMC) projects are being implemented to replace road transport through mechanical loading and conveying systems
- Avenue and peripheral plantation to arrest the propagation and dispersion of dust significantly.
- Installation of Wind barriers for dust trapping.
- Plantation on inactive OB Dumps to minimize soil erosion;
The existing statutory environmental framework provides safeguards to minimize the adverse environmental impacts of mining on the native environment.
Before commencement of mining, all mines must obtain Environmental Clearance (EC) from MoEF&CC for which, a detailed Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) is carried out, and accordingly a comprehensive Environment Management Plan (EMP) with all safeguards is prepared.
All mitigation measures are to be taken up by coal companies, for which funds are earmarked in project reports/schemes/mine closure plans/revenue and capital budgets of respective projects.
Thus, the present system of regulating environmental matters through MoEF&CC and CPCB/ SPCBs has an inbuilt mechanism in place for environmental protection in and around coal mining areas
Way forward
India needs to address the energy issues through clean coal and take advantage of the presence of interested private players in the mining sector.
Coal energy needs to transform by taking into account environmental factors like reducing carbon footprint, global warming, climate change, renewable and cleaner energy, etc.
Source: https://www.clearias.com/coal-mining-india/





Post a Comment for "Demerits of Continuous Miner N in Indian Coal Mines"